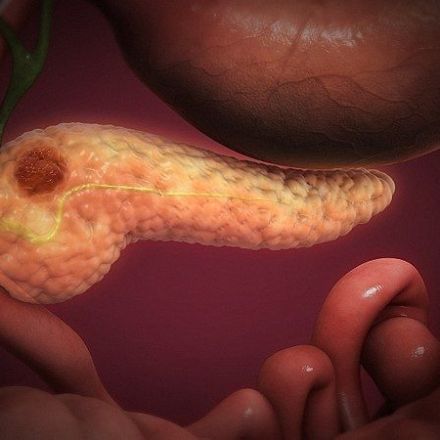
While current immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies are largely ineffective against pancreatic cancer, scientists in the U.S. have now identified an immune checkpoint molecule that could represent a promising immunotherapeutic target for this tumor type. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center-led team found that V-domain immunoglobulin suppressor of T cell activation (VISTA) is preferentially expressed at high levels in pancreatic cancer, when compared with melanoma tumors.
Continue reading...

No comments:
Post a Comment