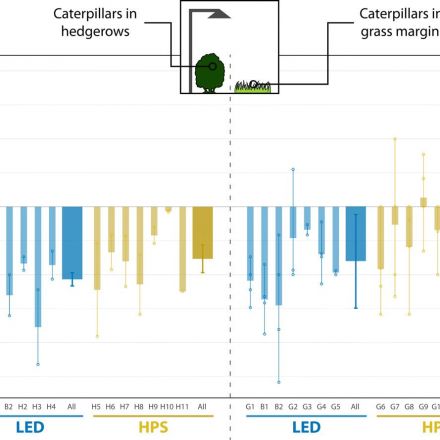
Reported declines in insect populations have sparked global concern, with artificial light at night (ALAN) identified as a potential contributing factor. Despite strong evidence that lighting disrupts a range of insect behaviors, the empirical evidence that ALAN diminishes wild insect abundance is limited. Using a matched-pairs design, we found that street lighting strongly reduced moth caterpillar abundance compared with unlit sites (47% reduction in hedgerows and 33% reduction in grass margins) and affected caterpillar development. A separate experiment in habitats with no history of lighting revealed that ALAN disrupted the feeding...
Continue reading...


No comments:
Post a Comment